Otoplasty in Turkey at Dr. Pilus: Everything You Need to Know
If you're considering otoplasty, also known as ear surgery, you're not alone. Many people are unhappy with the size, shape, or positioning of their ears, and otoplasty can help to address these concerns. At Dr. Pilus, we offer high-quality otoplasty procedures that can help you achieve the look you desire.
What Is Otoplasty?
Otoplasty is a surgical procedure that is used to reshape the ear. This can include correcting the position of the ears, reducing their size, or improving their shape. Otoplasty can be performed on people of all ages, from young children to adults. The procedure is typically performed on an outpatient basis and can take anywhere from 1-2 hours.
Why Turkey is a Popular Destination for Otoplasty
If you're considering otoplasty, Turkey is a great destination to consider. Here's why:
High-quality facilities and skilled surgeons
Turkey is home to many world-class medical facilities and skilled surgeons, making it an ideal destination for otoplasty. At Dr. Pilus, we pride ourselves on offering the highest quality care to our patients, with a focus on safety, comfort, and results.
Affordable cost
One of the biggest advantages of getting otoplasty in Turkey is the affordable cost. Compared to many other countries, otoplasty in Turkey is much more cost-effective, without compromising on quality.
Tourist-friendly destinations
Turkey is also known for its stunning tourist destinations, from the beaches of Antalya to the historic city of Istanbul. By combining your otoplasty procedure with a vacation, you can enjoy a relaxing and rejuvenating experience while also achieving the look you desire.
At Dr. Pilus, we offer a range of otoplasty procedures to meet your unique needs. Our skilled surgeons use the latest techniques and technologies to ensure the best possible results. Whether you're looking to correct the position of your ears, reduce their size, or improve their shape, we can help.

Pre-Surgery: Consultation And Planning
Before the surgery, patients will have a consultation with Dr. Pilus to discuss their goals and expectations. During this consultation, the surgeon will explain the procedure in detail and answer any questions the patient may have. The surgeon will also examine the patient's ears and recommend the best course of action based on the patient's individual needs.
Selecting The Right Surgeon
Selecting the right surgeon is crucial for a successful Otoplasty procedure. Dr. Pilus is committed to providing patients with the highest level of care and attention, ensuring that each patient receives personalized treatment and achieves the best possible results.
Understanding The Procedure
Otoplasty is typically performed under local anesthesia, and the procedure can take anywhere from 1-2 hours to complete. The surgeon will make an incision behind the ear and reshape the cartilage to create the desired look. In some cases, the surgeon may also remove excess skin and tissue. The incisions will then be closed with sutures, and the patient's head will be wrapped with a bandage.
Choosing The Appropriate Technique For Your Needs
Dr. Pilus offers a variety of Otoplasty techniques, including incisionless Otoplasty, which involves the use of sutures to reshape the ear without making an incision. This technique results in less scarring and a quicker recovery time. During the consultation, the surgeon will recommend the best technique for the patient's needs.
Preparing For The Surgery: What To Do And What To Avoid
Patients will be given specific instructions on how to prepare for the Otoplasty procedure, including what to do and what to avoid. It is important to follow these instructions carefully to ensure a smooth and successful procedure.
In conclusion, Otoplasty in Turkey at Dr. Pilus offers patients a safe and effective way to improve the appearance of their ears. With the help of skilled surgeons, state-of-the-art facilities, and affordable costs, patients can achieve their desired look and feel more confident. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and take the first step towards a new you.
The Otoplasty Procedure
Otoplasty, also known as ear surgery, is a cosmetic surgery procedure that aims to reshape and reposition the ears to achieve a more balanced and proportionate appearance. This procedure can correct various ear irregularities, such as protruding or excessively large ears, asymmetry, and deformities caused by injury or birth defects.
Anesthesia Options
Otoplasty is typically performed under local anesthesia with sedation or general anesthesia, depending on the surgeon's preference and the patient's health condition. Local anesthesia with sedation is usually preferred for children and adults who are anxious or uncomfortable with the surgery. General anesthesia is recommended for patients who require extensive correction or have medical conditions that make them ineligible for local anesthesia.
The Surgical Process Step-By-Step
The otoplasty procedure usually takes about 2-3 hours to complete, depending on the extent of the correction required. Here is a step-by-step process of what to expect during the surgery:
Anesthesia Administration - The anesthesia will be administered to the patient according to the surgeon's preference and the patient's condition.
Incision Placement - The surgeon will make an incision behind the ear or in the natural crease where the ear meets the head to access the cartilage.
Cartilage Reshaping - The cartilage will be reshaped using surgical techniques such as scoring, folding, and suturing to achieve the desired shape and position.
Skin Removal and Closure - If necessary, excess skin will be removed, and the incision will be closed with dissolvable sutures or surgical glue.
Dressing Application - A dressing or headband will be applied to the ears to protect and support them during the initial healing phase.
Common Complications And How To Avoid Them
Like any surgery, otoplasty carries some risks and potential complications, including bleeding, infection, hematoma, scarring, and changes in sensation. To minimize the risk of these complications, it is crucial to follow the surgeon's pre- and post-operative instructions carefully.
Before the surgery, the surgeon will evaluate the patient's health condition and medical history to ensure they are suitable candidates for the procedure. They will also provide instructions on what to do and what to avoid before the surgery, such as stopping smoking and taking certain medications.
After the surgery, the patient should avoid strenuous activities, wearing tight-fitting clothing or accessories that may put pressure on the ears, and exposing the ears to excessive heat or moisture. They should also keep the incision area clean and dry and attend all follow-up appointments to monitor the healing progress.
In conclusion, otoplasty is a safe and effective procedure that can improve the appearance and function of the ears. Dr. Pilus in Turkey offers high-quality facilities, skilled surgeons, and affordable costs for patients seeking otoplasty. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about how we can help you achieve your desired look.

Recovery And Post-Surgery Care
After your otoplasty procedure at Dr. Pilus, it is essential to take proper care to ensure a smooth and comfortable recovery. In this section, we will discuss what to expect during the recovery period and provide tips for a successful post-surgery care.
What To Expect During The Recovery Period
It is normal to experience some discomfort and mild pain following the surgery, but this can usually be managed with pain medication prescribed by your surgeon. Your ears will be wrapped in a soft, supportive bandage that will help keep them in place and promote healing. You may also be required to wear a headband or a special garment over your ears for a few days.
Swelling, bruising, and redness around the ears are common, and these symptoms typically subside within a week or two. Some patients may also experience temporary numbness or sensitivity around the ears, which should also resolve over time.
Tips For A Smooth Recovery
To ensure a smooth and comfortable recovery, it is important to follow your surgeon's post-surgery care instructions carefully. This may include taking prescribed medications, avoiding strenuous physical activities and sports for a few weeks, and avoiding sleeping on your side or touching your ears. You should also avoid any activities that could cause pressure or tension on your ears, such as wearing tight hats or headbands.
It is also essential to keep your ears clean and dry to prevent infection. Your surgeon will provide detailed instructions on how to care for your ears during the recovery period, including when you can resume normal activities such as showering or washing your hair.
Post-Surgery Care Instructions
Following your otoplasty surgery at Dr. Pilus, our team will provide you with detailed post-surgery care instructions to ensure a successful recovery. Some of the instructions may include:
- Taking pain medication as prescribed
- Applying ice packs to reduce swelling and bruising
- Wearing a headband or a special garment over your ears as instructed
- Keeping your ears clean and dry
- Avoiding strenuous physical activities and sports for a few weeks
- Avoiding sleeping on your side or touching your ears
- Following up with your surgeon for a post-surgery check-up and removal of stitches or bandages
By following these instructions carefully and taking good care of yourself, you can help ensure a smooth and successful recovery from your otoplasty surgery at Dr. Pilus.
In conclusion, otoplasty is a safe and effective procedure that can help you achieve a more aesthetically pleasing appearance and boost your self-confidence. At Dr. Pilus, we offer high-quality otoplasty surgery performed by skilled surgeons in state-of-the-art facilities at an affordable cost. With our commitment to patient satisfaction and care, you can trust us to help you achieve your desired results.
If you are considering otoplasty surgery in Turkey, contact us today to schedule a consultation with one of our experienced surgeons.
Results And Long-Term Outcomes
After an otoplasty procedure, patients can expect to see immediate results in the appearance of their ears. However, it's important to note that the final results may not be fully visible until several months after the surgery. During the initial recovery period, patients may experience swelling, bruising, and discomfort. As the body continues to heal, these side effects will gradually subside, revealing the final results.
Maintaining The Results Over Time
In order to maintain the results of an otoplasty over time, patients should follow their surgeon's post-surgery care instructions closely. This may include wearing a headband or compression garment to help support the ears and promote healing. Patients should also avoid any strenuous activities or heavy lifting for several weeks following the surgery. In addition, it's important to keep the ears clean and free from infection by following proper hygiene practices.
What To Do If You Are Not Satisfied With The Outcome
While otoplasty is generally a safe and effective procedure, there is always a possibility that the final results may not meet the patient's expectations. If this occurs, patients should speak with their surgeon to discuss their concerns and explore any options for revision surgery or other corrective measures. It's important to have realistic expectations for the procedure and to communicate openly with the surgeon throughout the process.
Overall, otoplasty can be an effective way to improve the appearance of the ears and boost a patient's confidence. By working with a skilled and experienced surgeon, patients can achieve the desired results with minimal risk of complications. If you're considering otoplasty in Turkey, Dr. Pilus offers a range of techniques and personalized care to help you achieve your aesthetic goals. Contact us today to schedule a consultation and learn more about your options.
The Average Cost Of Otoplasty In Turkey
The cost of otoplasty in Turkey varies depending on the surgeon, the technique used, and the extent of the surgery. On average, the cost of otoplasty in Turkey ranges from $1,500 to $3,500, which is significantly lower than the cost of the procedure in other countries like the United States and the United Kingdom. This is one of the main reasons why Turkey has become a popular destination for cosmetic surgeries, including otoplasty.
Financing Options
At Dr. Pilus, we understand that the cost of otoplasty surgery may be a concern for some patients. That's why we offer financing options to make the procedure more accessible to everyone. Our financing options include installment plans and payment plans with low interest rates. Our team can help you choose the best financing option that suits your needs and budget.
The Benefits Of Otoplasty
Improved Self-Esteem And Confidence Otoplasty can improve your self-esteem and confidence by correcting any ear irregularities that make you feel self-conscious. Many patients report feeling more comfortable and confident in social situations after otoplasty.
Enhanced Appearance And Proportionality
Otoplasty can also enhance the appearance and proportionality of the ears. By reshaping the ears, otoplasty can create a more aesthetically pleasing look that complements the rest of your facial features.
Better Hearing And Ear Function
In some cases, otoplasty can improve hearing and ear function by correcting any structural abnormalities that may be interfering with your hearing.
Who Is A Good Candidate For Otoplasty?
Otoplasty, also known as ear surgery, is a cosmetic procedure designed to reshape and reposition the ears. It is commonly used to treat protruding or asymmetrical ears, as well as other ear deformities. While the procedure is typically performed on children and adolescents, it is also a suitable option for adults.
The Impact Of Age And Genetics On The Procedure
The ideal age for otoplasty is between the ages of 5 and 14, when the ears have fully developed but are still pliable enough to allow for reshaping. However, the procedure can be performed on adults as well. Genetics can also play a role in ear deformities and asymmetry, making otoplasty an effective solution for those with inherited ear shape issues.
Otoplasty Vs. Other Ear Procedures
It is important to note that otoplasty is not the same as other ear surgeries, such as earlobe repair or reconstruction, which are typically performed to correct damage or deformities in the earlobes. Otoplasty is specifically designed to reshape the ear cartilage to improve the overall appearance of the ear.
How Otoplasty Differs From Other Ear Surgeries
Otoplasty differs from other ear surgeries in its focus on reshaping the ear cartilage. The procedure typically involves making an incision behind the ear, removing or reshaping excess cartilage, and then repositioning the ear closer to the head. This results in a more natural-looking ear that is in better proportion to the face.
Choosing The Right Procedure For Your Needs
If you are considering otoplasty, it is important to consult with a qualified cosmetic surgeon who can help you determine the right procedure for your needs. Your surgeon will consider factors such as your age, ear shape, and overall health to determine the best approach for achieving your desired results.
Success Stories Of Patients Who Underwent Otoplasty At Dr. Pilus' Clinic
Many patients who undergo otoplasty surgery at Dr. Pilus' clinic are thrilled with the results. They report a significant improvement in their self-esteem and confidence, and are happy with the overall appearance of their ears. Some even say that their hearing has improved as a result of the surgery.
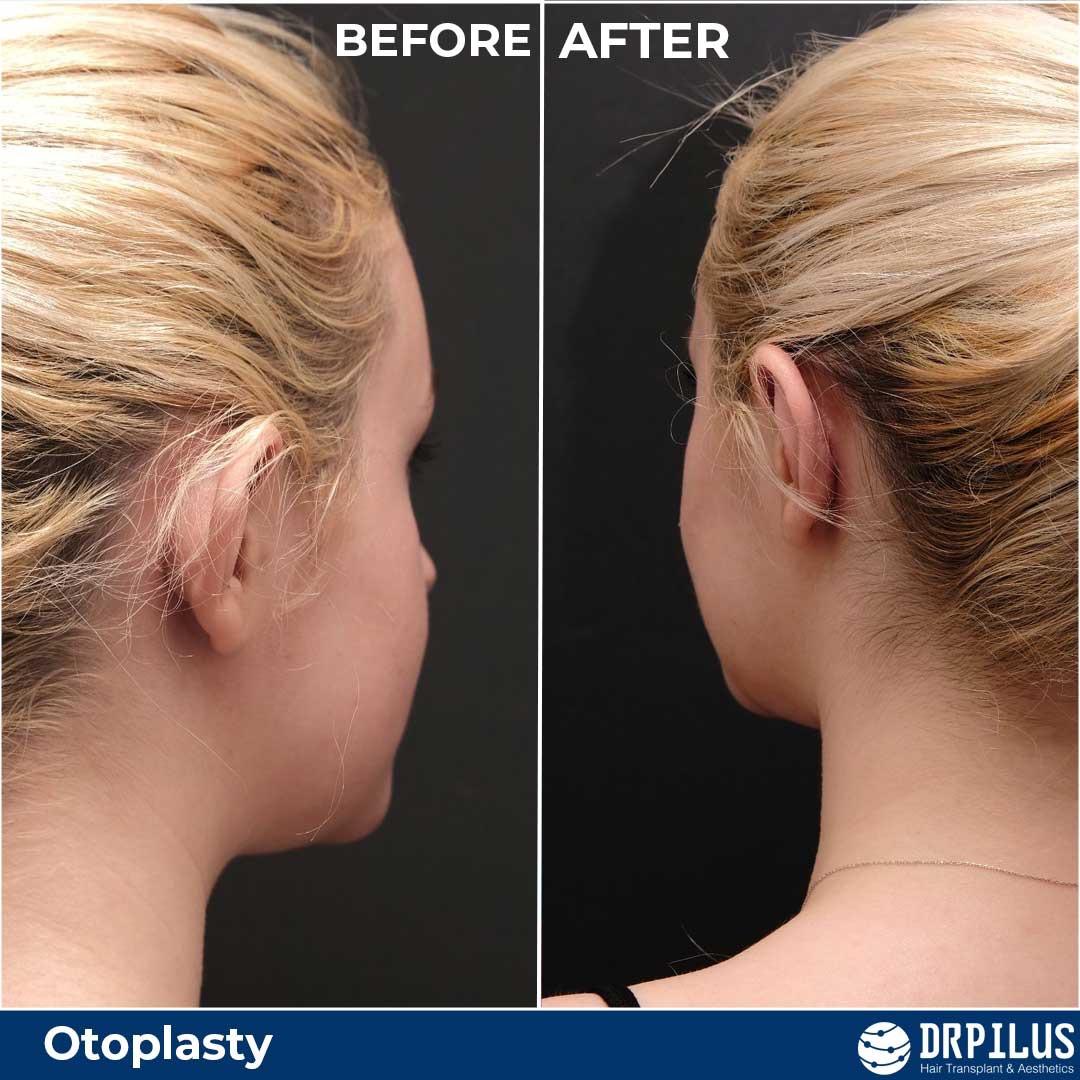
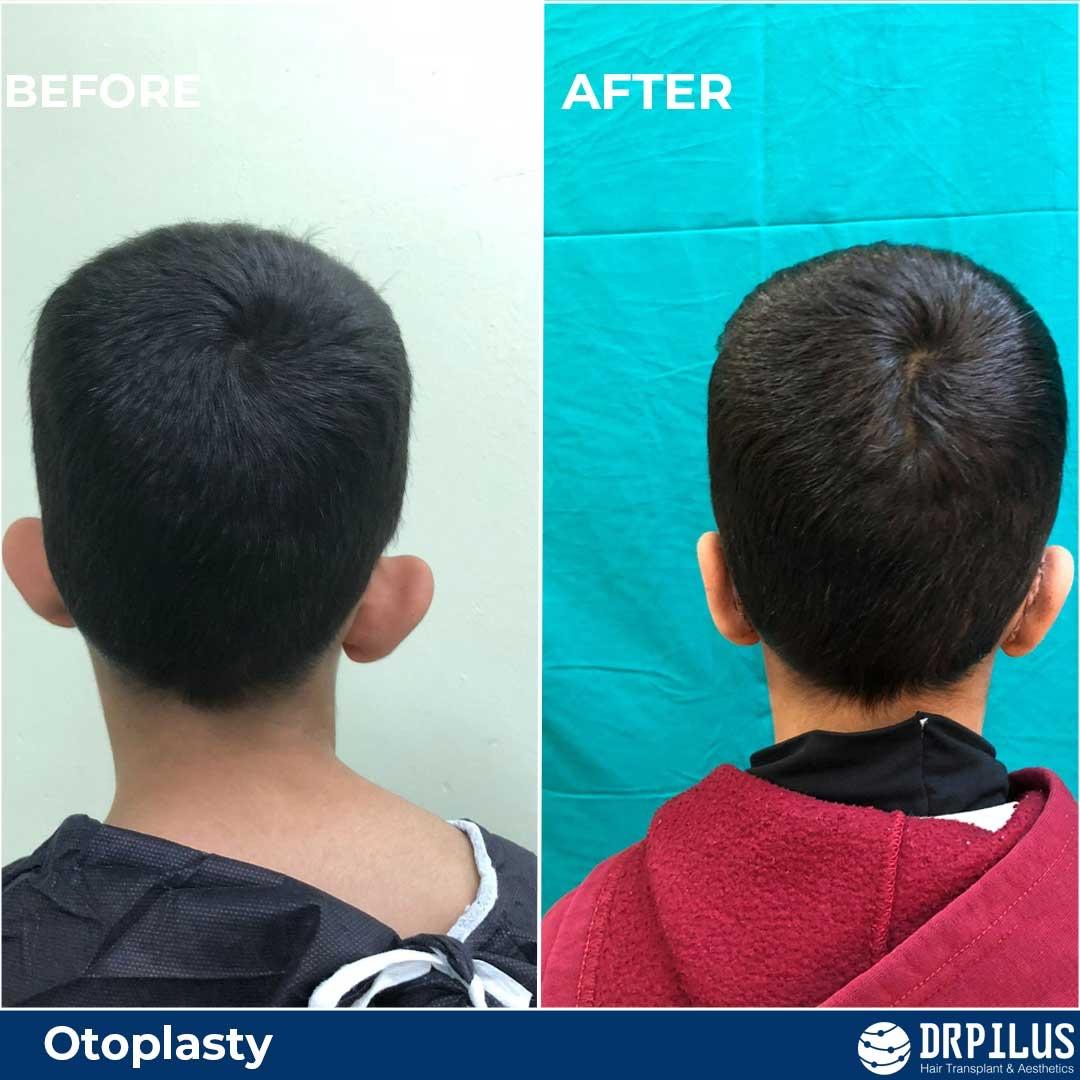
Before And After Photos: Real Patient Stories
Before and after photos of previous patients can be a helpful tool when considering otoplasty surgery. These photos give you an idea of what to expect in terms of results and can help you visualize the potential changes to your appearance. At Dr. Pilus' clinic, before and after photos are available to show you what other patients have experienced and how their ears were transformed.
Traveling To Turkey For Otoplasty
Turkey is a popular destination for medical tourism due to its high-quality medical facilities and affordable prices. Many people choose to travel to Turkey for otoplasty surgery because it is often less expensive than in their home country. Additionally, Turkey is known for its highly skilled and experienced plastic surgeons, making it a desirable destination for those seeking cosmetic surgery.
Travel And Accommodation Arrangements
If you are considering traveling to Turkey for otoplasty surgery, it is important to make travel and accommodation arrangements well in advance. Dr. Pilus' clinic can help you with all of your travel and accommodation needs, including booking flights and arranging transportation to and from the airport. They also offer a range of accommodation options, from budget-friendly hotels to luxury apartments.
Tips For Traveling To Turkey For Medical Procedures
If you are planning to travel to Turkey for medical procedures such as otoplasty surgery, it is important to take certain precautions to ensure a safe and successful trip. Some tips include researching your chosen medical facility and surgeon thoroughly, obtaining any necessary visas or documentation, and bringing any required medications or medical equipment with you. Dr. Pilus' clinic can provide additional guidance on how to prepare for your trip and what to expect during your stay in Turkey.
Faq About Otoplasty In Turkey
How Long Does The Procedure Take?:
The duration of otoplasty surgery can vary depending on the complexity of the case and the technique used. On average, the procedure takes between 1 to 2 hours.
Is Otoplasty Painful?:
During the procedure, patients receive anesthesia, so they do not experience any pain. However, it is normal to experience some discomfort and swelling in the first few days after surgery. Your surgeon may prescribe medication to help manage the pain.
How Long Is The Recovery Period?:
The recovery period varies from patient to patient, but generally takes about 1-2 weeks. Most patients can return to their normal activities, including work and school, within 7-10 days after surgery. However, it is important to avoid any strenuous activities or contact sports for several weeks.
Can I Wear Glasses Or Earrings After The Surgery?:
It is recommended that patients avoid wearing glasses or earrings for at least 4 weeks after surgery to avoid putting pressure on the ears. After that time, it is usually safe to wear glasses or earrings again, but you should consult with your surgeon to confirm when it is safe to do so.
Is It Safe To Travel After The Surgery?:
While it is generally safe to travel after otoplasty, it is important to give yourself enough time to recover before undertaking any long journeys. Your surgeon will provide you with specific post-surgery instructions and recommendations, which may include avoiding air travel for a certain period of time after surgery. It is important to follow these instructions carefully to ensure a smooth recovery.